Learning sparse transformations through backpropagation
Many transformations in deep learning architectures are sparsely connected. When such transformations cannot be designed by hand, they can be learned, even through plain backpropagation, for instance in attention mechanisms. However, during learning, such sparse structures are often represented in a dense form, as we do not know beforehand which elements will eventually become non-zero. We introduce the adaptive, sparse hyperlayer, a method for learning a sparse transformation, parametrized sparsely: as index-tuples with associated values.
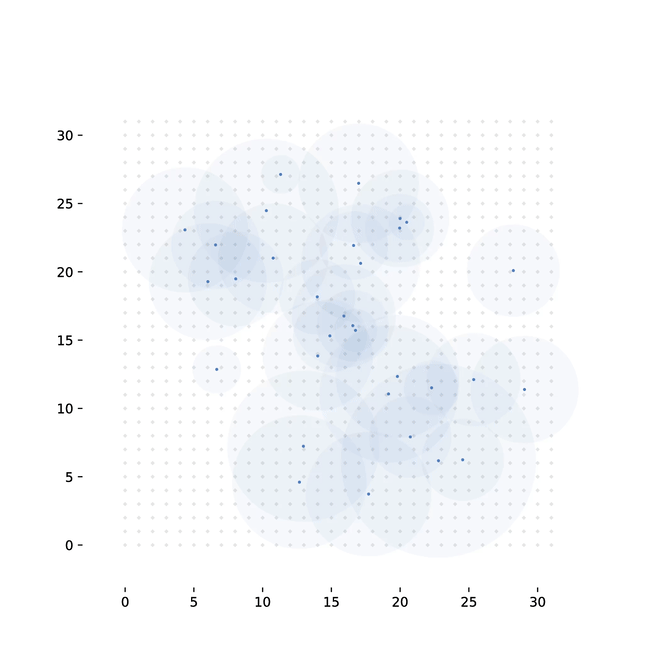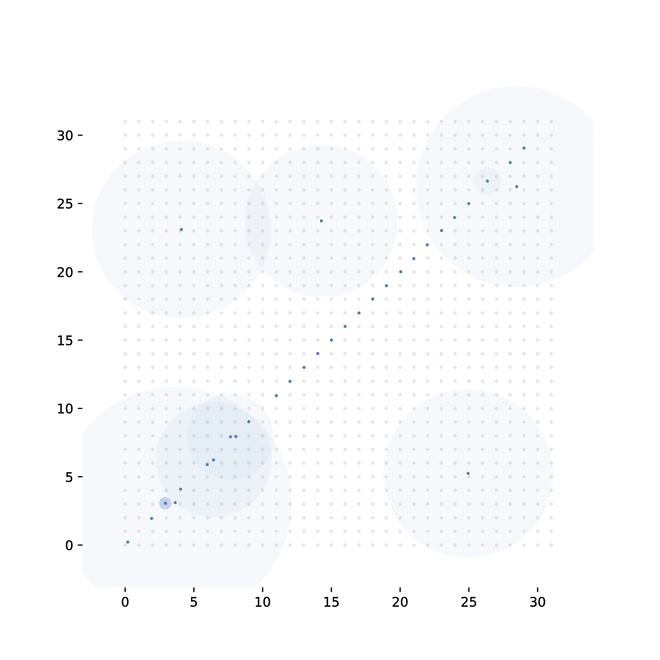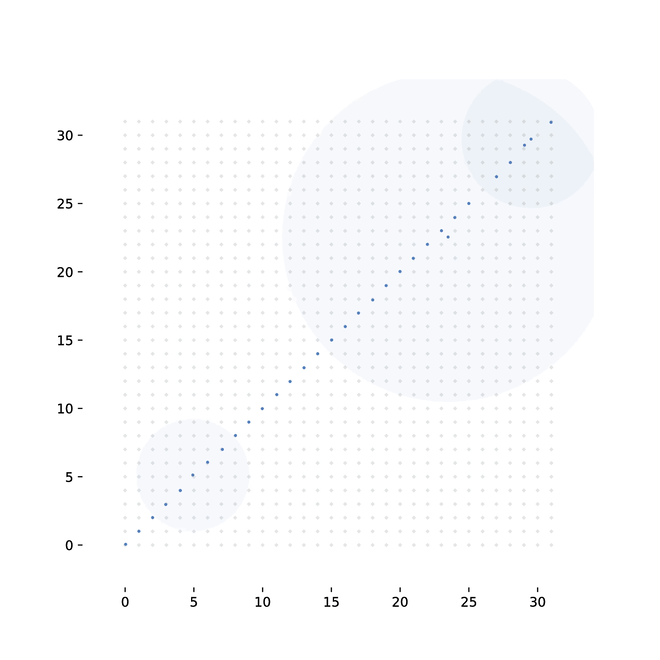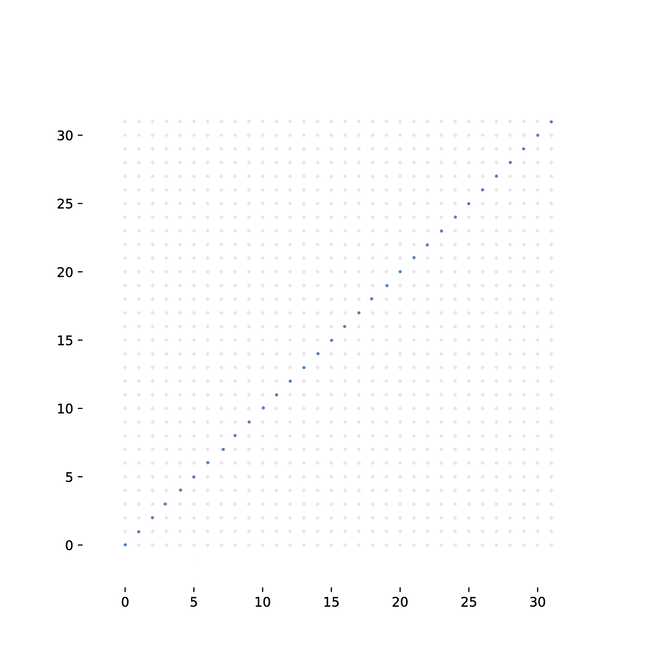
To overcome the lack of gradients from such a discrete structure, we introduce a method of randomly sampling connections, and backpropagating over the randomly wired computation graph. To show that this approach allows us to train a model to competitive performance on real data, we use it to build two architectures. First, an attention mechanism for visual classification. Second, we implement a method for differentiable sorting: specifically, learning to sort unlabeled MNIST digits, given only the correct order.